Mikhail Gnesin is a Soviet and Russian composer, musician, public figure, critic, teacher. For a long creative career, he received many state awards and prizes.
He was remembered by his compatriots first of all as a teacher and educator. He carried out pedagogical and musical-educational work. Gnesin led circles in the cultural centers of Russia.
Childhood and youth
The composer's date of birth is January 21, 1883. Mikhail was lucky to be brought up in a primordially intelligent and creative family.
The Gnessins are representatives of a large family of musicians. They made a huge contribution to the cultural development of their native country. Little Mikhail was surrounded by solid talents. His sisters were listed as promising musicians. They were educated in the capital.
Mom, who had no education, did not deny herself the pleasure of singing and playing music. The charming voice of the woman especially amused Mikhail. Mikhail's younger brother became a professional performer. Thus, almost all family members realized themselves in creative professions.
When the time came, Mikhail was sent to the Petrovsky real school. During this period of time, he takes music lessons from a professional teacher.
Gnesin was attracted to improvisation. Soon he composes an author's piece of music, which received laudatory reviews from a music teacher. Mikhail was distinguished from his peers by great erudition. In addition to music, he was fond of literature, history, ethnography.
Closer to the 17th birthday, he was finally convinced that he wanted to become a musician and composer. The large family supported Michael's decision. Soon he went to Moscow to get an education.
The young man was extremely surprised when the teachers advised him to “bring up” knowledge. Family connections did not help Mikhail become a student at the conservatory. The Gnessin sisters studied at this educational institution.
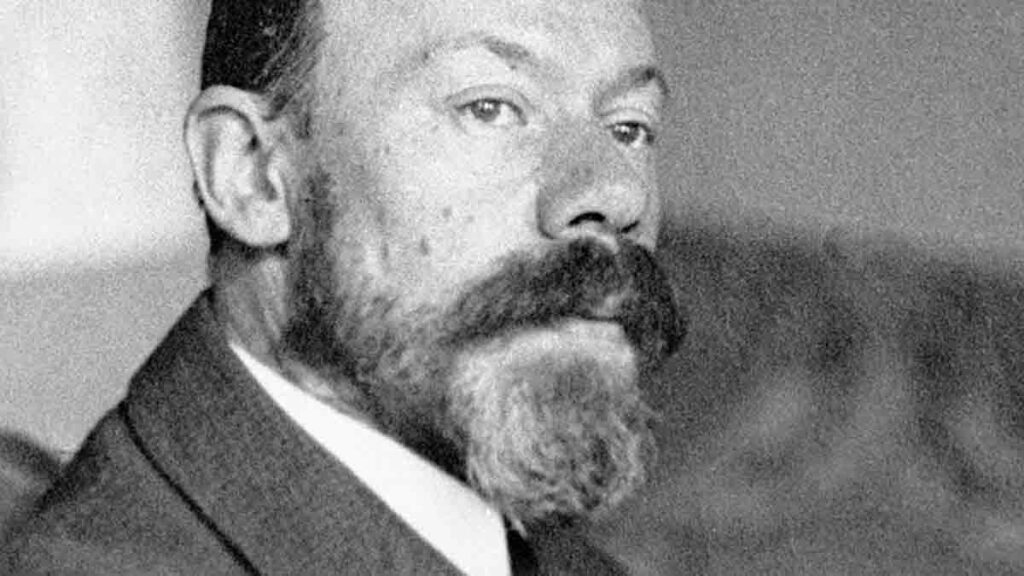

Then he went to the cultural capital of Russia. Mikhail showed the first works to the popular composer Lyadov. Maestro, rewarded the young man with flattering reviews of his works. He advised him to enter the St. Petersburg Conservatory.
Gnesin's admission to the conservatory
At the beginning of the new century, Mikhail Gnesin applied to the St. Petersburg Conservatory. The teachers saw talent in him, and he was enrolled in the Faculty of Theory and Composition.
The main teacher and mentor of the young man was the composer Rimsky-Korsakov. Gnesin's communication with the maestro had a strong influence on him. Until the death of Mikhail, he considered his teacher and mentor to be an ideal. It is not surprising that after the death of Rimsky-Korsakov, it was Gnesin who edited the last edition.
In 1905, a talented musician and aspiring composer took part in the revolutionary processes. In this regard, he was arrested and expelled from the conservatory in disgrace. True, a year later he was again enrolled in an educational institution.
During this period of time, he became part of the symbolist literary circle. Thanks to the holding of symbolic evenings, he managed to get acquainted with the brightest poets of the "Silver Age". Gnesin - was in the center of cultural life, and this could not be reflected in his early work.
He composes music for symbolist poems. Also during this period of time, he writes poignant novels. He develops a unique manner of presenting music.
Song works that Mikhail created to the words of the Symbolists, as well as other compositions of the so-called "Symbolist" period, are the most voluminous part of the maestro's legacy.
It was then that he developed an interest in Greek tragedy. New knowledge leads the composer to create a special musical pronunciation of the text. At the same time, the composer created music for three tragedies.
In the cultural capital of Russia, the active musical-critical and scientific activities of the maestro began. He is published in several magazines. Mikhail spoke excellently about the problems of modern music, its national characteristics in art, as well as the principles of symphony.
Mikhail Gnesin: educational activities of the composer
The composer's fame is growing. His works are of interest not only in Russia, but also abroad. After graduating from the conservatory, his name was inscribed on the board of outstanding graduates.
Everything would be fine, but Mikhail Gnesin considers noble enlightenment to be the main goal of his life. Stravinsky, who at that time was part of his circle of close friends, advised Gnesin to go abroad, since, in his opinion, Mikhail had nothing to catch in his homeland. The composer answers the following: "I will go to the provinces and will engage in education."
Soon he went to Krasnodar, and then to Rostov. The cultural life of the city has completely changed since the arrival of Gnesin. The composer had his own approach to the cultural ennoblement of the city.
He regularly organizes music festivals and lectures. With his help, several music schools, libraries, and later, a conservatory were opened in the city. Michael became the head of the educational institution. The First World War and the Civil War did not prevent the composer from realizing the most brilliant plans.
In the early 20s of the last century, he briefly settled in luxurious apartments in Berlin. The composer had every chance to take root in this country forever. At that time, European critics and music lovers were ready to accept the maestro and even grant him citizenship.
Gnesin's activities in Moscow
But, he was attracted by Russia. Some time later, together with his family, he permanently moves to Moscow to join the business started by his sisters.
Mikhail Fabianovich joins the life of the technical school. He opens a creative department and applies a new teaching principle there. In his opinion, it is necessary to engage in composing compositions with students immediately, and not after working out the theory. Later, the maestro will publish a whole textbook that will devote to this issue.
In addition, lessons for children were introduced at the Gnesins' school. Prior to this, the question of such a format of teaching was considered ridiculous, but Mikhail Gnesin convinced his colleagues of the expediency of studying with the younger generation.
Gnesin does not leave the walls of the Moscow Conservatory. He soon became dean of the new faculty of composition. In addition, the maestro leads the composition class.
Mikhail Gnesin: decline in activity under the onslaught of RAMP
At the end of the 20s, an aggressive offensive was launched by the musical proletarians - RAPM. The Association of Musicians takes root in cultural life and wins leadership positions. Many give up their position before the onslaught of representatives of the RAPM, but this does not apply to Mikhail.
Gnesin, who never kept his mouth shut, objected to RAMP in every possible way. Those, in turn, publish false articles about Mikhail. The composer is suspended from work at the Moscow Conservatory and even demanded the closure of the faculty he led. Mikhail's music in this period of time sounds less and less. They are trying to wipe him off the face of the earth.
The composer does not give up. He writes complaints to senior officials. Gnesin even turned to Stalin for support. The RAPM pressure ceased in the early 30s. Actually then the association was dissolved.
After the October Revolution, some musicians performed the immortal works of the composer. Gradually, however, the maestro's compositions sound less and less frequently. The poetry of the Symbolists also fell into the "black list", and at the same time, access to the stage was closed to the romances of the Russian composer written on their poems.
Michael decides to slow down. During this period of time, he practically does not compose new works. In the early 30s, he again appeared at the conservatory, but soon his faculty was closed again, because it was considered that he would not be of benefit to students. Gnesin feels frankly bad. The situation is further aggravated by the death of the first wife.
After these events, he decides to move to St. Petersburg. He is a professor at the conservatory. Michael's reputation is gradually restored. He enjoys great respect among students and in the teaching community. Strength and optimism return to him.
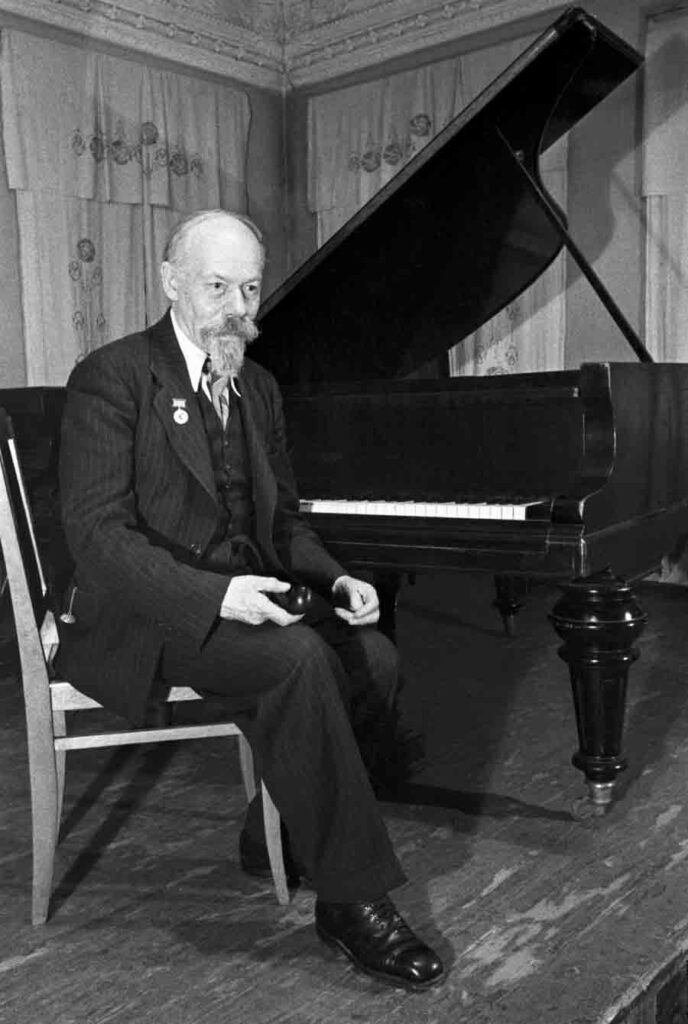

He continued to experiment with music. In particular, you can hear notes of folk music in his works. Then he was working on the creation of a book about Rimsky-Korsakov.
But, the composer only dreamed of a quiet life. At the end of the 30s, he learns that his younger brother was repressed and shot. Then the war comes, and Mikhail, together with his second wife, moves to Yoshkar-Ola.
Mikhail Gnesin: work at Gnesinka
In 42, he joined a group of musicians from the St. Petersburg Conservatory, who was taken to Tashkent. But the worst was yet to come. He learns about the death of his 35-year-old son. Michael sinks into depression. But, even in this difficult time, the composer composes a brilliant trio "In memory of our dead children." The maestro dedicated the composition to his tragically deceased son.
Sister Elena Gnesina, in the mid-40s of the last century, founded a new institution of higher education. She invites her brother to the university for a leadership position. He accepted the invitation of a relative and headed the department of composition. At the same time, his repertoire was replenished with the Sonata-Fantasy.
Details of the personal life of Mikhail Gnesin
Margolina Nadezhda - became the first wife of the maestro. She worked in the library and did translations. After meeting Mikhail, the woman entered the conservatory and trained as a singer.
In this marriage, the son Fabius was born. The young man was gifted as a musician. It is also known that he had a mental disorder that prevented him from realizing himself in life. He lived with his father.
After the death of his first wife, Gnesin took Galina Vankovich as his wife. She worked at the Moscow Conservatory. There were real legends about this woman. She was very erudite. Galina spoke several languages, she painted pictures, composed poetry and played music.
The last years of the composer's life
He went on a well-deserved rest, but even in retirement, Gnesin did not get tired of composing musical works. In 1956, he did publish the book Thoughts and Memories of N. A. Rimsky-Korsakov. Despite the great services to his homeland, his compositions sound less and less. He died of a heart attack on May 5, 1957.
Today, he is increasingly referred to as a "forgotten" composer. But, we must not forget that his creative heritage is original and unique. In the last 10-15 years, the works of the Russian composer have been performed much more often abroad than in their historical homeland.